iVABS, a VABS-based Structural Design Framework#
iVABS (namely integrated VABS), is a design framework for composite slender structures (also called composite beams) such as helicopter rotor blades, wind turbine blades, high aspect ratio wings, bridges, shafts, etc.
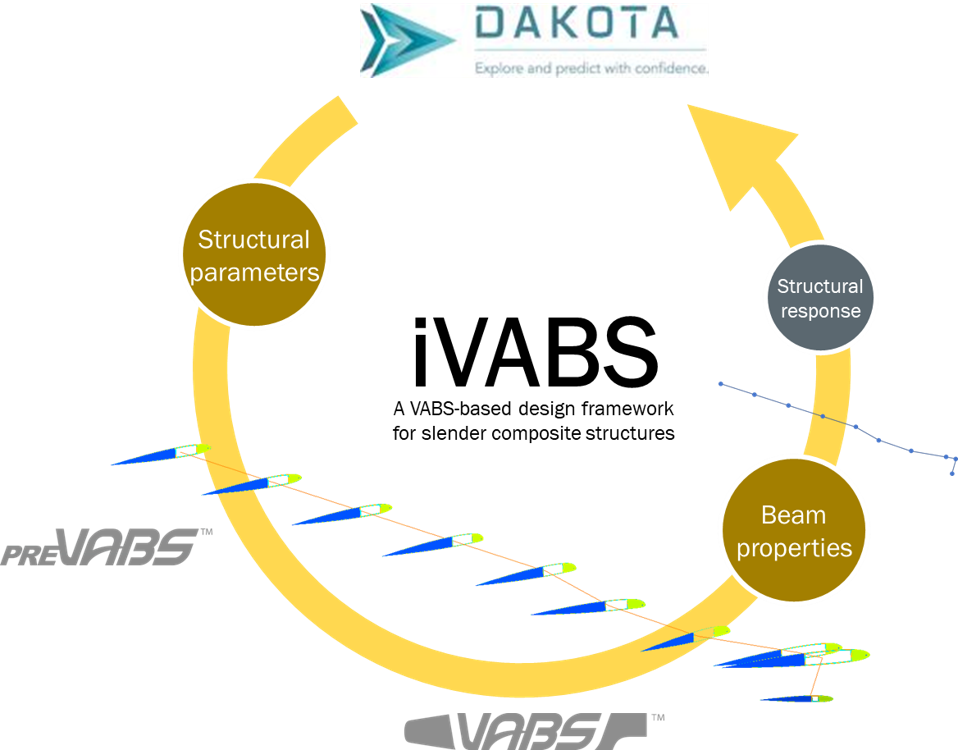
The iVABS framework.#
This framework bundles PreVABS, VABS, GEBT, Dakota, along with Python for integration among these codes and other codes.
PreVABS is a preprocessor to generate composite sections with ply-level details based on a few design parameters including sectional geometry, topology, and material.
VABS is a cross-sectional analysis code to to model composite slender structures as beams. It is resulting from decades of university research (Georgia Tech/Utah State/Purdue) sponsored by US Army.
GEBT is a geometrical exact nonlinear beam analysis code for computing linear or nonlinear, static or dynamic behavior of composite beams. This code can be replaced with more sophicated codes such as MBDyn, RCAS, DYMORE, CAMRAD II, etc.
Dakota is a multilevel, parallel, object-oriented framework for design optimization, parameter estimation, uncertainty quantification, and sensitivity analysis. .. This code can be easily replaced by another design and optimization framework such as OpenMADO.
SGIO is a collection of python scripts for integrating the codes needed in iVABS and the scripts can be modified to integrate other codes.
To make use of SGIO, Python3 along with necessary packages (particularly numpy, scipy, and pyyaml) should be installed and working on your computer.
Manual#
Contributing#
You are welcome to contribute to the iVABS documentation in the following ways:
Add an issue for bug reports or feature requests.
Start a new discussion if you need help running iVABS.
License#
iVABS (excluding VABS) and its documentation is copyrighted (C) 2021- by Purdue Research Foundation and is distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL) (version 2 or later, with an exception to allow for easier linking with external libraries).
VABS is a commercial code and a trial or paid license can be requested from AnalySwift.
Acknowledgement#
The iVABS team at the Purdue University (PoC: Prof. Wenbin Yu) completed the software development under the BAA project “Efficient High-Fidelity Framework for Structural Design and Optimization of Composite Lifting Bodies” funded by ERDC (PoCs: Dr. Robert Haehnel from U.S. Army ERDC and Dr. Joon W. Lim from U.S. Army DEVCOM AvMC).