Build Cross-section in Abaqus and Export to VABS#
Brief Instruction#
Overall, the process is similar to creating a meshed beam cross-section part in Abaqus.
Part:
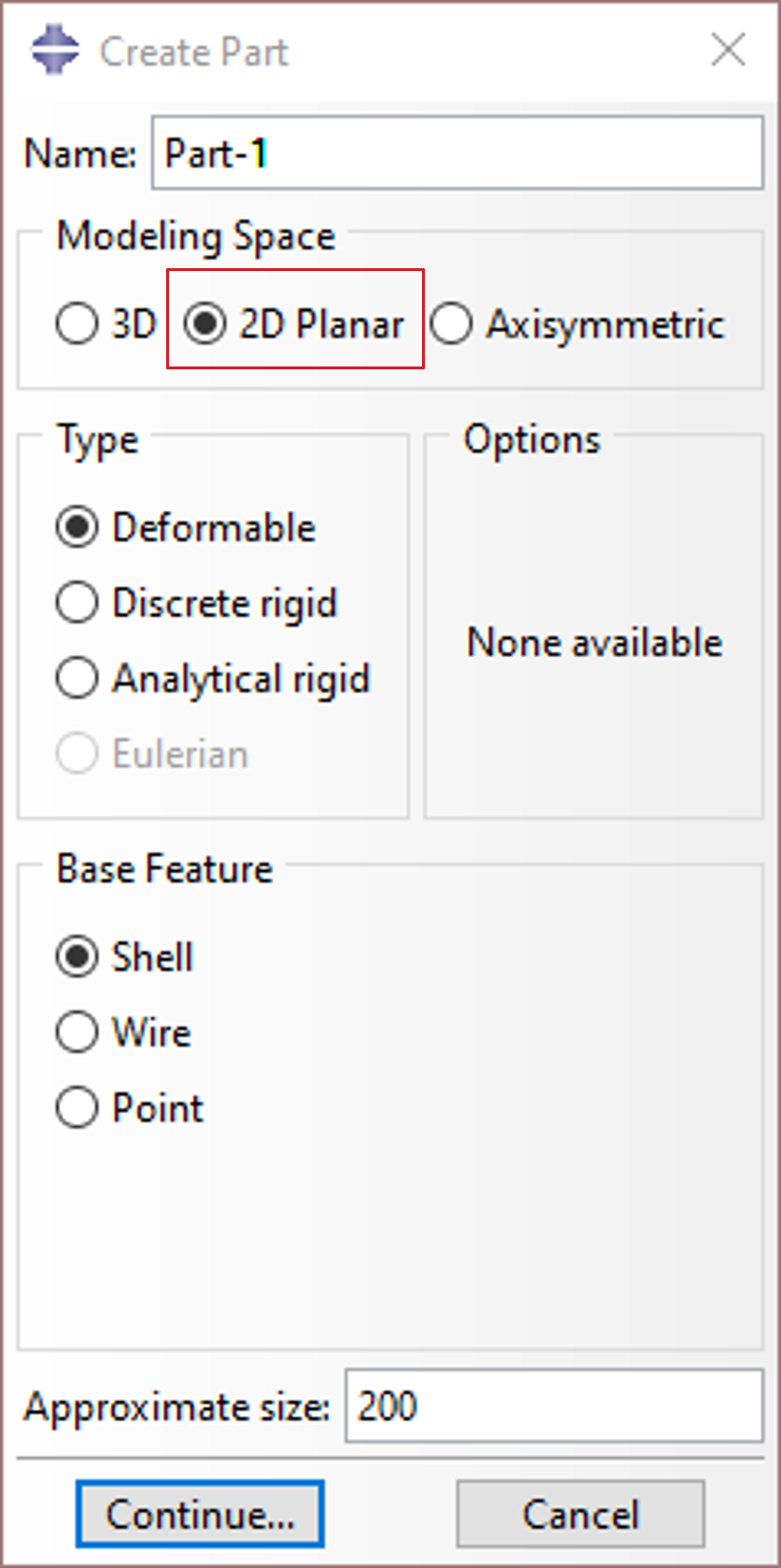
Modeling space: 2D planar
Type: Deformable
Base feature: Shell
Property:
Material: Any
Section: Composite layup (Solid, Homogeneous)
Mesh: Any
Write the Abaqus model to an INP file.
Convert the INP file to a VABS input file using the command:
python -m sgio convert <filename>.inp <filename>.sg -ff abaqus -tf vabs
Detailed Instruction#
Part module#
As a cross-section of a slender structure, it is natural to create a “Deformable” “Shell” part in the “2D Planar” modeling space.
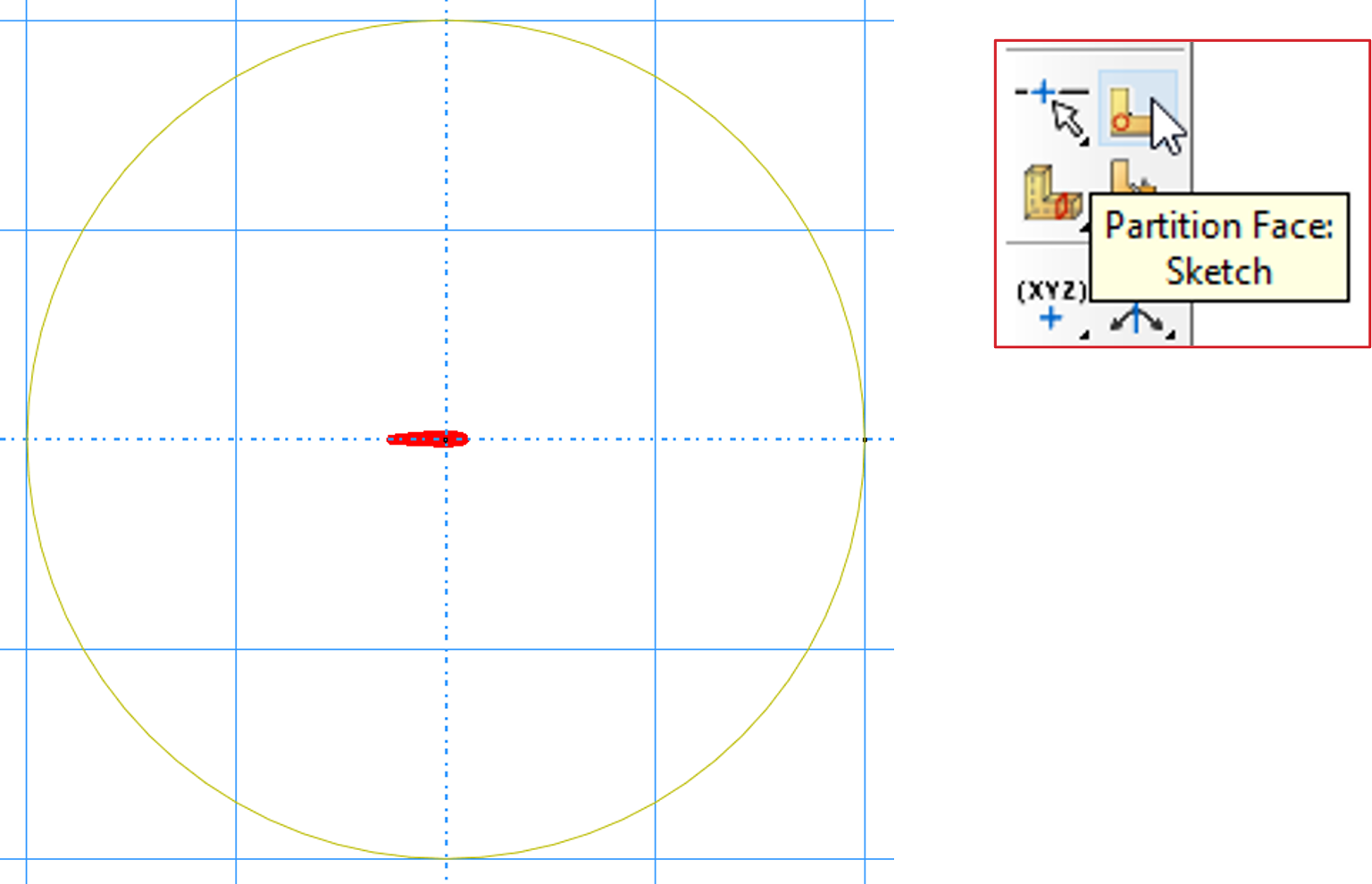
Composite structures can have different materials in different regions. A useful tip is to create a base shape, such as a circle, large enough to cover the entire cross-section. Then, use the “Partition Face” tool to divide the base shape into regions.
Property#
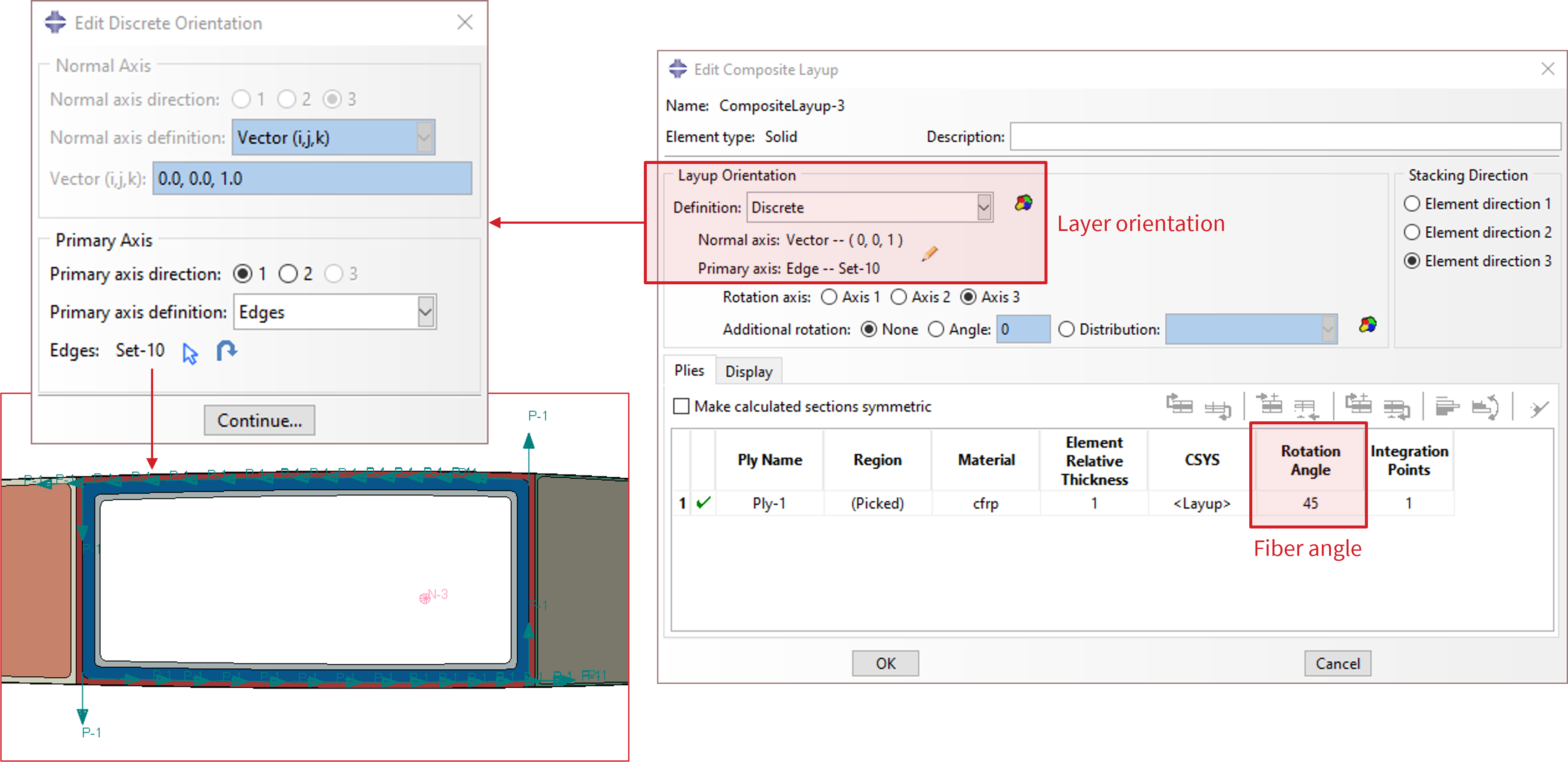
Any type of material can be used for the cross-section, such as isotropic, engineering constants, or orthotropic. VABS requires local orientation data and allows additional in-plane rotations (fiber angle) for each layer. Hence, it is required to use the “Composite Layup” section type. Here are instructions for setting up a “Composite Layup” section:
Each section contains only one ply.
Layer orientation is defined by assigning the local \(y\) axis, while the local \(x\) axis is always normal to the cross-sectional plane. For a composite layer, the local \(y\) axis is usually set to be tangent to a base line.
To set the fiber angle for each layer, use the column “Rotation Angle”.
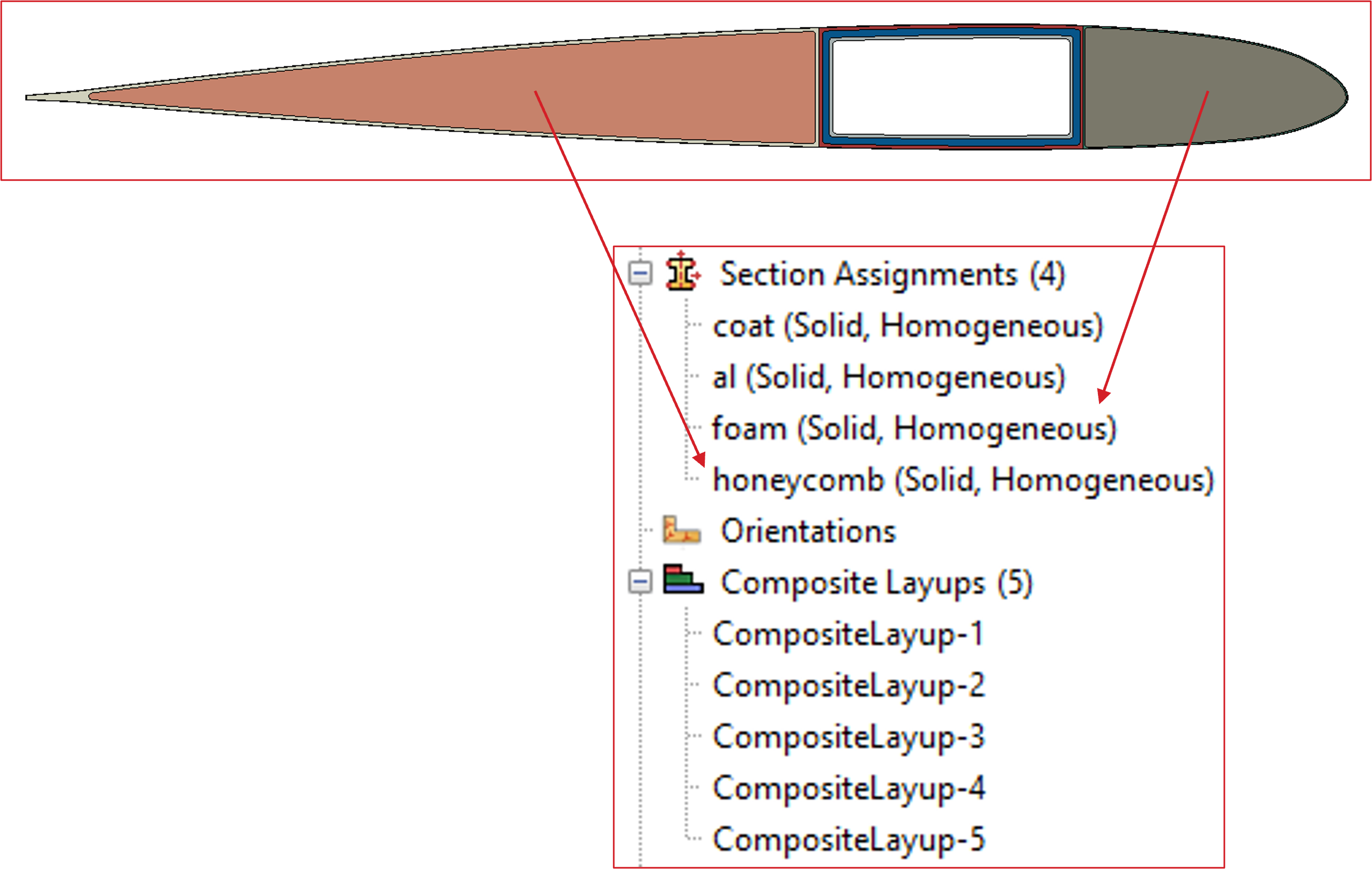
It is okay to use the “Composite Layup” section for all materials. However, if a material is isotropic and no local orientation and fiber angle are needed, then it is also acceptable to use the “Solid” section.
Mesh#
There is no restriction on meshing.
File export#
Create a job and write the model to an INP file. Then use the command below to convert the INP file to a VABS input file:
python -m sgio convert <filename>.inp <filename>.sg -ff abaqus -tf vabs
By default, the Timoshenko beam model will be used.
To use the Euler-Bernoulli beam model, add the option -m bm1:
python -m sgio convert <filename>.inp <filename>.sg -ff abaqus -tf vabs -m bm1
To see help messages, use the command:
python -m sgio convert -h