Overview
OpenSG is a general-purpose software for multiscale modeling of structures and materials. It allows you to efficiently and accurately bridge microscale details at the macroscale. It is powered by the Mechanics of Structure Genome (MSG) theory and has been implemented with FEniCS.
The first step in using OpenSG is deciding the fidelity-level of your target structural analysis. Are you targeting a beam model in GXBeam or BeamDyn? Are you targeting a solid model of a printed circuit board ANSYS? OpenSG supports all three types of structural finite element models, namely Beam, Shell, and Solid models.
The structure gene (SG) is defined as the mathematical building block of a structure. So the next step is identifying the SGs in your structure and what level of fidelity you will use to mesh it. It can be meshed with either 1D line elements, 2D Quad/Tri elements, or 3D Hex/Tet elements.
Then the Key Features of OpenSG can utilized.
Key Features and Capabilities
Homogenization: The MSG framework calculates the effective material, shell, or beam properties of complex structures by analyzing the SGs. This is known as homogenization.
Structural Analysis: These effective properties are then used in a global structural analysis (e.g., Abaqus shell model, BeamDyn beam model, ANSYS solid model) to determine the overall structural response.
Dehomogenization (Optional): Finally, the global results are used in a dehomogenization step to calculate the local stress and strain fields within the complex structure.
Panel buckling (Optional): OpenSG has been designed to use dehomogenization results to solve eigen value buckling problems.
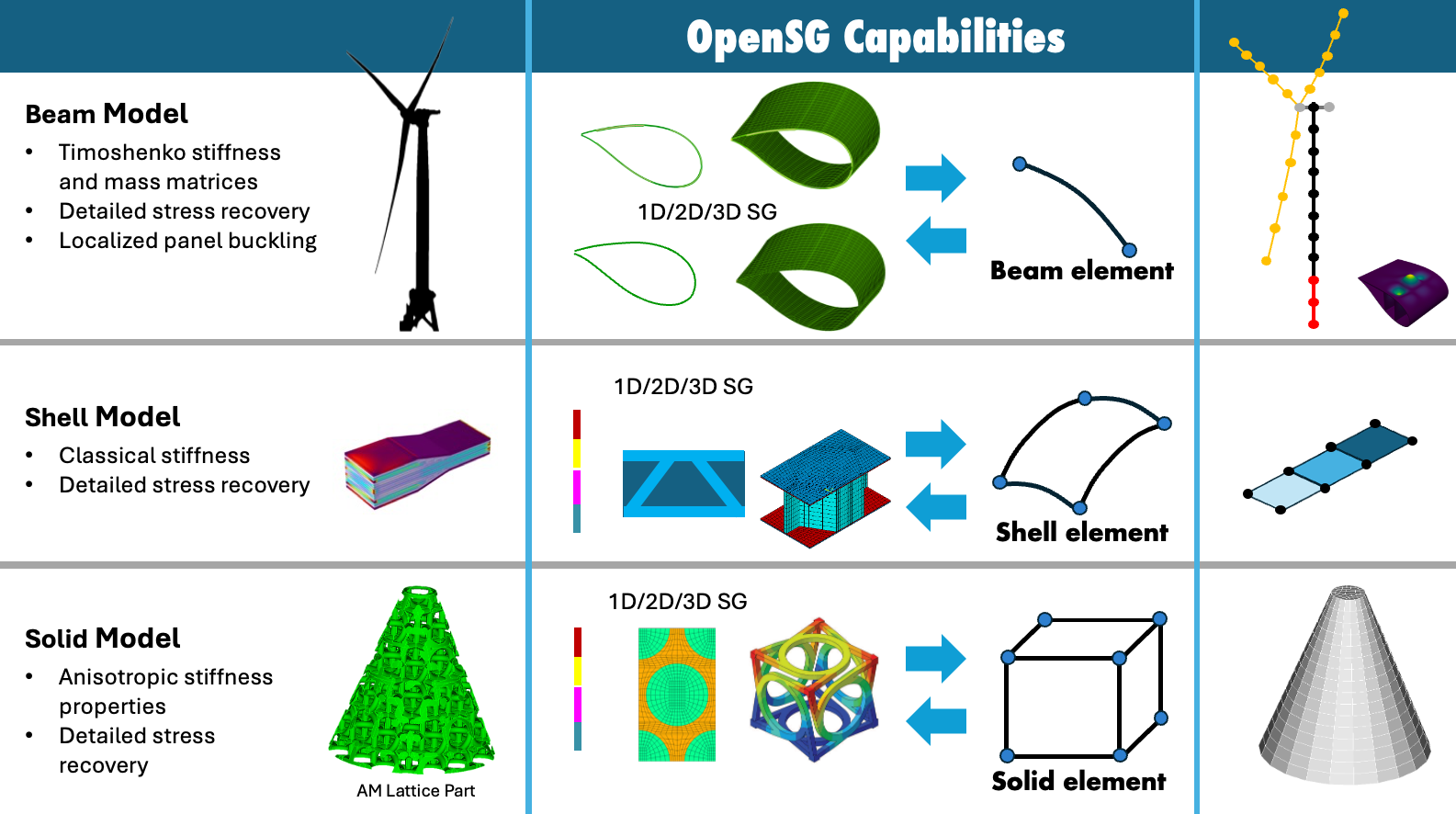
Fig. 1 OpenSG capabilities.
Applications
Tapered laminated composite beams such as wind blades
Composite material and structural analysis
Additively manufactured parts
Propellers
Metal lattice structures (Eiffel Tower or additively manufactured lattice structures for example)
Airplane wings
Propellers
Offshore jacketed structures
Long tapered tubes
Non prismatic bridges
Non prismatic beams or columns
Unit cells of metals, composites or foams
Laminates, sandwich structures, or corrugated structures
And more